Scaling is essential for database management, especially as businesses grow and handle increasing volumes of data. To ensure databases can handle more traffic, we need to understand how scaling works. There are two primary methods: horizontal scaling and vertical scaling. Each has its own approach, benefits, and challenges. Here’s a breakdown of how databases scale and the differences between these two strategies.
1. What is Database Scaling?
Database scaling is the process of adjusting the infrastructure that supports a database to improve its performance, handle more traffic, and accommodate larger datasets. As databases handle increasing requests from applications or users, they need more resources to maintain speed and reliability.
The two main methods of scaling are:
- Vertical Scaling: Increasing the capacity of a single server.
- Horizontal Scaling: Adding more servers to share the load.
Let’s dive into these in more detail.
2. Vertical Scaling (Scale-Up)
Vertical scaling involves upgrading the current database server’s hardware to increase its capacity. This usually means adding more CPU, RAM, or storage to the existing server. In simpler terms, it’s like boosting your computer’s specifications to make it run faster and handle more applications at once.
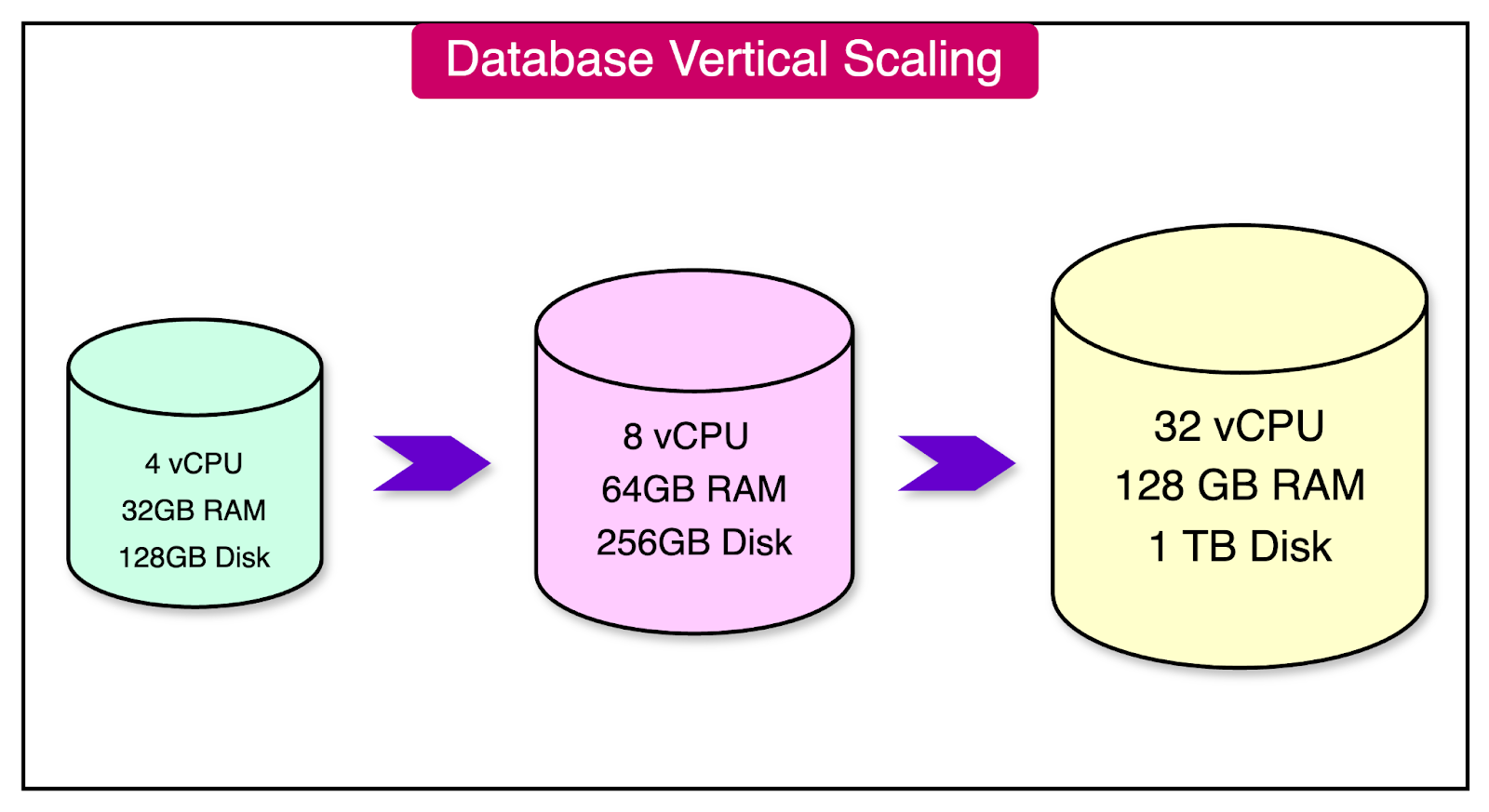
Benefits of Vertical Scaling
- Simplicity: With vertical scaling, you don’t need to manage multiple servers, making it easier to maintain and administer.
- Software Compatibility: Many applications and databases are easier to configure for vertical scaling since you’re just upgrading one machine.
Drawbacks of Vertical Scaling
- Hardware Limits: There’s a physical limit to how much you can upgrade a single server.
- Higher Costs: High-performance hardware becomes expensive as you increase CPU, memory, and disk space.
- Single Point of Failure: Since everything relies on a single server, if it fails, the entire database can go down.
When to Use Vertical Scaling
Vertical scaling is often suitable for smaller applications or for handling short-term, modest increases in demand. If your database’s performance bottleneck can be solved by adding more CPU or RAM, then vertical scaling might be the simplest and most cost-effective solution.
3. Horizontal Scaling (Scale-Out)
Horizontal scaling involves adding more servers to your infrastructure, distributing the database across multiple machines. Instead of relying on a single powerful server, you have a collection of servers that share the workload.
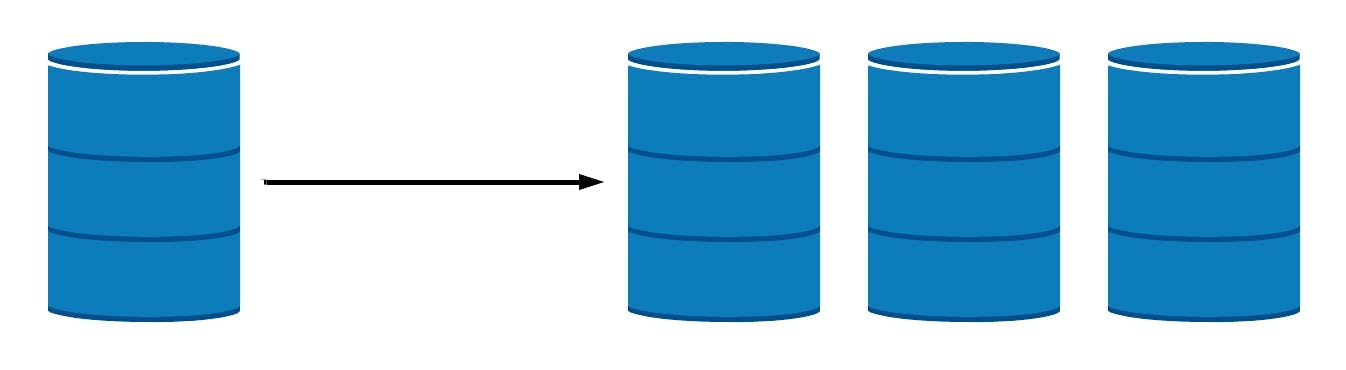
Benefits of Horizontal Scaling
- Better Performance: By distributing data across multiple machines, horizontal scaling can significantly improve the database’s performance, even under heavy loads.
- Higher Fault Tolerance: With multiple servers, the database can stay operational even if one server fails.
- Infinite Scalability: Theoretically, you can keep adding servers to handle an increasing load.
Drawbacks of Horizontal Scaling
- Complexity: Managing a distributed system can be complicated. Data consistency, synchronization, and network latency must be carefully managed.
- Infrastructure Costs: While individual servers might be cheaper, the total cost of infrastructure, networking, and administration can add up.
- Data Sharding: To distribute data, it often needs to be “sharded,” or split across servers. Sharding can make querying data more complex and may require significant re-engineering.
When to Use Horizontal Scaling
Horizontal scaling is ideal for large applications or high-traffic sites where data storage and processing demands are continually growing. Large companies like Google, Facebook, and Amazon rely heavily on horizontal scaling for their vast data needs.
4. Vertical vs. Horizontal Scaling: A Quick Comparison
| Aspect | Vertical Scaling | Horizontal Scaling |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Adding more power to one server | Adding more servers |
| Complexity | Simple to implement | More complex to manage |
| Limitations | Limited by hardware capacity | Scalable with more servers |
| Fault Tolerance | Single point of failure | Higher redundancy |
| Cost | Higher per-server cost | Lower per-server cost, higher total costs |
| Best For | Short-term scaling needs, smaller apps | High-traffic, large-scale applications |
5. Choosing the Right Scaling Solution

When deciding between vertical and horizontal scaling, consider:
- Current and Future Load: If you foresee rapid growth, horizontal scaling may offer a more sustainable solution.
- Budget: If immediate budget constraints exist, a modest upgrade to a single server (vertical scaling) may suffice.
- Technical Resources: Horizontal scaling requires more expertise to manage a distributed system.
- Downtime Tolerance: For critical applications, horizontal scaling offers better redundancy to maintain uptime.
6. Combining Horizontal and Vertical Scaling
In practice, many businesses combine both methods to optimize performance and cost-effectiveness. For instance, you might start with vertical scaling, then adopt horizontal scaling as your database outgrows a single server. This hybrid approach leverages the simplicity of vertical scaling with the long-term scalability of horizontal scaling.
Conclusion
Understanding database scaling and the differences between horizontal and vertical approaches is essential for choosing the best option based on your needs. Both scaling methods have distinct advantages and limitations, so the choice depends on factors like growth trajectory, budget, and fault tolerance requirements. Proper scaling ensures your database can keep up with user demands, maintain high performance, and grow with your business.
Whether you’re just starting or scaling up, knowing these fundamentals will help you make informed decisions to optimize database performance and reliability.
